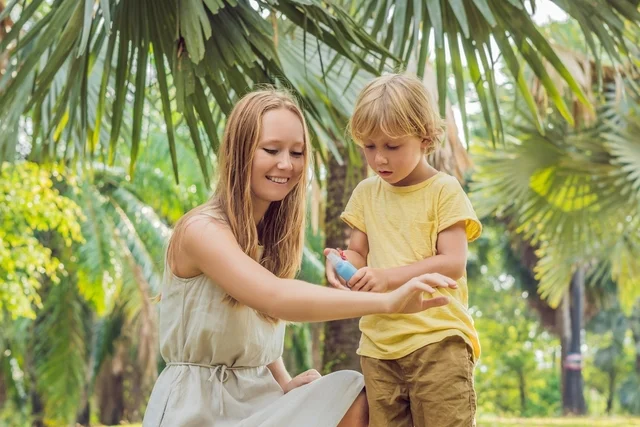
The Different Types of Repellents
When it comes to protecting ourselves from pesky bugs and insects, repellents are our best friends. They come in various forms, each with its own unique features and benefits. In this article, we will explore the different types of repellents available in the market, discuss which one to choose, and provide tips on how to use them effectively.
The most used repellents are:
1. DEEP
The action of DEEP repellent is centered on its active ingredients, such as DEET (N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide) or other insect repellent substances. DEET is one of the most common ingredients in insect repellents and works by interfering with the odor receptors of insects, making the person less attractive to them.
When applied to the skin, DEEP repellent forms a layer that confuses insects, making them less likely to land or bite. Instead, insects tend to move away from the person who applied the repellent.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of DEEP repellent may vary depending on factors such as the concentration of active ingredients, product formulation, and environmental conditions. Additionally, the duration of protection may also vary, usually ranging from a few hours to several hours, depending on the specific formula and user activity.
While DEEP repellent may offer effective protection against insect bites, it is always advisable to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take other protective measures, such as wearing protective clothing and avoiding areas known to have insect infestations.
2. Icaridina
The action of icaridin-based insect repellent is similar to that of DEET (N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide), but with some differences. Icaridin, also known as picaridin, is a commonly used active ingredient in insect repellents. It acts as an effective repellent against a variety of insects, including mosquitoes, flies, ticks, and other biting arthropods.
Like DEET, icaridin works by interfering with the odor receptors of insects, making it difficult for them to detect humans or other animals as food sources. This makes insects less attracted and, consequently, less likely to land on human skin and bite.
Icaridin is often preferred by some people over DEET for various reasons, including a less strong odor and a less oily sensation on the skin. Additionally, icaridin tends to have better skin irritation tolerance compared to DEET at similar concentrations.
The duration of protection offered by icaridin may vary depending on the product concentration and environmental conditions, but it generally provides protection for several hours after application.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using icaridin-based repellents, applying the product as recommended and avoiding contact with the eyes, mouth, and irritated skin areas. It is also advisable to reapply the repellent as needed, especially after swimming or excessive sweating.
3. IR 3535
The IR3535 repellent is an active ingredient commonly found in insect repellents, known by its chemical name, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate. It is effective in protecting against bites from a variety of insects, including mosquitoes, ticks, flies, and other arthropods.
IR3535 acts as an insect repellent by interfering with the odor receptors of insects, making it difficult for them to detect humans as targets. This makes people less attractive to insects and reduces the likelihood of bites.
One of the reasons why IR3535 is often recommended for pregnant women is due to its overall safety. When used according to the manufacturer’s instructions, IR3535 is considered safe for use during pregnancy. Unlike some other insect repellents, such as DEET, IR3535 is not absorbed through the skin in large quantities, making it a preferred choice for pregnant women concerned about potential adverse effects on the fetus.
Additionally, IR3535 generally has a milder fragrance and is less likely to cause skin irritation than some other insect repellents, which may be more comfortable for pregnant women, whose skin may be more sensitive during pregnancy.
However, as with any product, it is important for pregnant women to consult their doctors before using any insect repellent, including those containing IR3535, to ensure that it is safe for them and for their babies.
4 . Natural oils
There are several essential oils known for their insect-repellent properties. Some of the most effective ones include:
-
Citronella oil: This oil is extracted from the citronella plant and is effective against mosquitoes, especially Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which can transmit diseases such as dengue, Zika, and chikungunya. Citronella oil is often used in candles, lotions, and insect repellent sprays.
-
Lemon eucalyptus oil: This oil is derived from the leaves of certain eucalyptus species and has insect-repellent properties. It is effective against mosquitoes, ticks, and flies.
-
Lavender oil: In addition to its pleasant aroma, lavender oil also has insect-repellent properties. It is especially effective against mosquitoes and can also help soothe skin irritated by insect bites.
-
Peppermint oil: This oil has a strong smell that can repel insects, including mosquitoes, flies, and ants.
-
Tea tree oil (melaleuca): Known for its antiseptic and antimicrobial properties, tea tree oil also has insect-repellent effects, especially against mosquitoes.
Regarding duration time, repellent oils generally do not have the same longevity as synthetic repellents such as DEET or picaridin. They may need to be reapplied more frequently to maintain their effectiveness. Duration time can vary depending on the concentration of the oil, environmental conditions, and type of insect. In general, it is recommended to reapply the repellent oil every one to three hours to ensure continuous protection against insect bites.
5. Physical repellents
Physical repellents are methods of protection against insects that do not involve the use of chemicals or repellent substances. Instead, they rely on physical barriers to prevent insects from coming close or making contact with the skin. Here are some options for physical repellents:
-
Long-sleeved shirts and pants: Wearing clothing that covers most of the body can be an effective way to protect against insect bites. Especially in areas where insects are a concern, wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants can prevent insects from making contact with the skin.
-
Mosquito nets: Using mosquito nets around the bed or resting area can provide a physical barrier to prevent insects, such as mosquitoes, from reaching you while sleeping.
-
Screens on windows and doors: Installing screens on windows and doors can help prevent insects from entering your home or living space, offering protection against mosquitoes, flies, and other insects.
-
Fans: Keeping fans running in outdoor areas where you spend time can help deter flying insects, such as mosquitoes, by creating an airflow that makes it difficult for them to fly towards you.
-
Ultrasonic repellents: These devices emit high-frequency sounds that are purportedly irritating to insects, deterring them from the area. However, the effectiveness of these repellents is still subject to debate and research.
While physical repellents can offer some protection against insect bites, it’s important to remember that they may not be as effective as chemical repellents in certain situations and in areas with heavy insect infestations. Therefore, it’s a good idea to consider a combination of protection methods, including both physical and chemical repellents, to ensure comprehensive protection against insects.
How to apply repellent correctly?
Applying insect repellent correctly is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Here are some tips on how to apply repellent properly:
-
Read the label: Before applying any repellent, carefully read the label instructions. This includes information on how to apply the product, how often to reapply it, and any precautions to take.
-
Choose the right repellent: Make sure to choose a repellent suitable for the type of insects you want to repel and for the duration of outdoor activity.
-
Apply evenly: Apply the repellent evenly on all exposed areas of the skin. Avoid applying it on cuts, wounds, or irritated skin areas.
-
Avoid sensitive areas: Avoid applying repellent near the eyes, mouth, and mucous membranes. If applying on children, apply the product on your own hands first and then spread it on the child’s skin.
-
Do not apply under clothing: Do not apply insect repellent under clothing, as this can result in excessive skin exposure or inhalation of chemicals.
-
Do not overapply: Use only the amount needed to cover exposed skin. Applying an excessive amount of repellent will not increase its effectiveness and may increase the risk of skin irritation.
-
Reapply as needed: Reapply the repellent as recommended in the product instructions. This is especially important if you are sweating a lot or swimming, as the effectiveness of the repellent may diminish over time.
-
Wash hands after application: After applying the repellent, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially if dealing with children.
By following these guidelines, you can apply insect repellent effectively and safely, helping to protect you and your family from unwanted insect bites.