Tonsillitis can significantly disrupt a person’s daily life due to the uncomfortable symptoms that accompany this condition. An intense sore throat can make it difficult to eat and stay hydrated, resulting in loss of appetite and dehydration. Additionally, fatigue associated with fever and other symptoms can affect energy and ability to concentrate, impacting performance at work, school and daily activities. Difficulty communicating due to pain when speaking can also limit participation in social and professional interactions, leading to temporary isolation.1. Sore Throat
One of the most common symptoms of tonsillitis is a sore throat. The throat may feel scratchy, painful, or tender, making it uncomfortable to swallow or speak. The severity of the sore throat can vary from mild to severe.
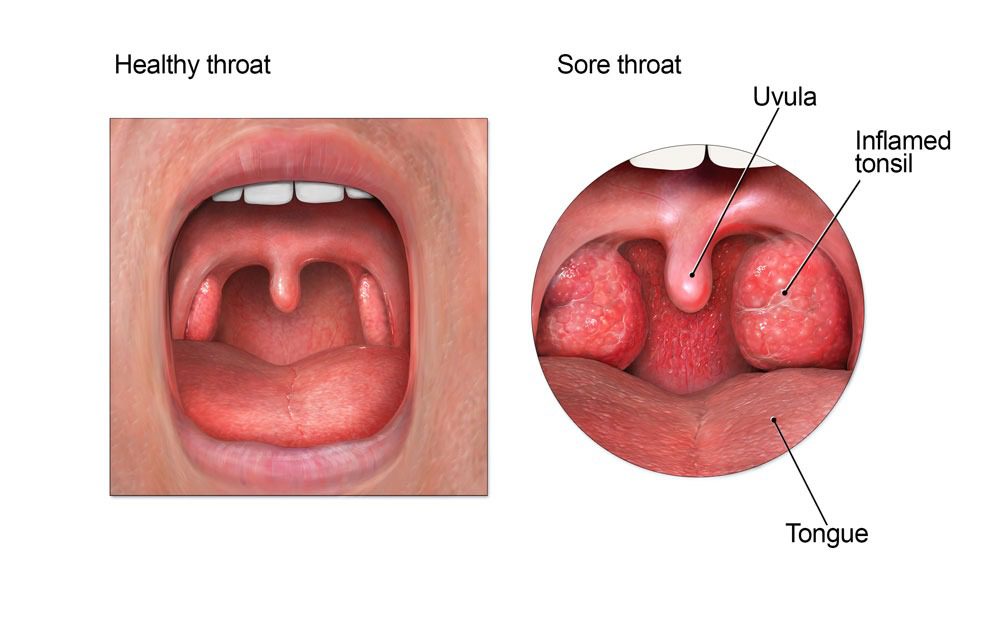
What is tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, which are two small almond-shaped organs located at the back of the throat, one on each side. These glands are part of the lymphatic system and play an important role in defending the body against infections, filtering bacteria and viruses that enter through the mouth and nose.
There are two main types of tonsillitis: viral and bacterial. Viral tonsillitis is more common and is usually caused by viruses, such as those responsible for the flu or the common cold. Bacterial tonsillitis is often caused by bacteria, with Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus) being the most common cause. Bacterial tonsillitis, often known as streptococcal tonsillitis, is treated with antibiotics.
Symptoms of tonsillitis can include severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, swollen tonsils, fever, body aches and a red throat. In some cases, plaques of pus may develop on the tonsils.
What are the symptoms of tonsillitis?
The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary in severity and depend on the underlying cause (viral or bacterial). Here are some common symptoms associated with tonsillitis:
- Sore throat: Sore throat is one of the most prominent symptoms of tonsillitis and can range from mild to severe.
- Difficulty swallowing: Inflammation of the tonsils can cause difficulty and pain while swallowing food and liquids.
- Tonsil swelling: The tonsils may become swollen and, in some cases, develop pus-filled spots.
- Red throat: The throat may become red and inflamed due to infection.
- Fever: Tonsillitis is often accompanied by fever, especially in cases of bacterial infection.
- Headache: Many people with tonsillitis experience headaches, caused by the body’s inflammatory response to the infection.
- General discomfort: Symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of unwellness may be present.
- Body aches: Some individuals may report muscle and joint pains during an episode of tonsillitis.
- Hoarse voice: Tonsil inflammation can affect the vocal cords, resulting in hoarseness.
- Cough: Coughing may occur due to irritation in the throat.
It’s important to note that viral and bacterial tonsillitis can present similar symptoms, making it challenging to differentiate them based solely on symptoms. Accurate diagnosis often requires evaluation by a healthcare professional, who may conduct tests to determine the specific cause of tonsillitis. If you suspect tonsillitis, it is advisable to seek medical guidance for proper treatment.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of tonsillitis is typically established by a healthcare professional through a physical examination and an assessment of the symptoms presented by the patient. During the examination, the doctor checks the throat for signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling of the tonsils, and the presence of pus. Additionally, measuring body temperature is common to check for fever, a common symptom of tonsillitis.
In some cases, the doctor may conduct additional tests to confirm the cause of tonsillitis. This may include a rapid strep antigen test to detect the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes, a common bacterium associated with bacterial tonsillitis. In more complex situations or when the diagnosis is unclear, blood tests and throat cultures may be requested to provide additional information about the nature of the infection. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate treatment and ensure effective recovery.
How to treat tonsillitis?
The treatment of tonsillitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In the case of viral tonsillitis, antibiotics are usually not necessary, as viral infections often resolve on their own. Rest, adequate fluid intake, analgesics, and antipyretics are recommended to alleviate symptoms such as pain and fever. Additional measures, such as gargling with warm saltwater, can help soothe the sore throat.
For bacterial tonsillitis, especially if caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, treatment often involves the use of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. It is crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the treatment is finished, to ensure complete eradication of the infection. In addition to medications, proper rest, hydration, and analgesics may be recommended to alleviate symptoms while the body fights the infection. In cases of recurrent or severe tonsillitis, surgical removal of the tonsils, known as a tonsillectomy, may be considered. This procedure is reserved for specific situations and is generally recommended only when other treatment options are not effective.
What teas can help?
While teas won’t cure tonsillitis, some can provide relief from symptoms. The best tea for tonsillitis is typically one that offers anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and soothing properties. Here are some options:
- Chamomile Tea: Chamomile is known for its anti-inflammatory and calming properties. It may help alleviate sore throat and reduce inflammation.
- Ginger Tea: Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties and can help relieve throat pain. Additionally, ginger may have beneficial effects in reducing nausea.
- Peppermint Tea: Peppermint has analgesic properties and can help alleviate throat irritation. The steam from hot peppermint tea can also be comforting.
- Licorice Tea: Licorice root has anti-inflammatory properties and may help soothe an irritated throat. However, it should be consumed in moderation.
- Echinacea Tea: Some people believe that echinacea can boost the immune system, aiding in the recovery from infections, including tonsillitis.
Adding honey to tea can provide additional benefits, as honey has antimicrobial properties and can help soothe the throat. However, it’s essential to remember that these teas are complementary and do not replace proper medical treatment. If you are dealing with tonsillitis, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the most appropriate treatment.