Arthritis and arthrosis are two terms often used interchangeably to describe joint-related conditions. While they share similarities, it’s important to understand the differences between the two. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of arthritis and arthrosis, helping you differentiate between the two and providing insights into managing these conditions.
Arthritis: A Comprehensive Overview
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing various joint disorders that cause inflammation and pain. It refers to the inflammation of one or more joints, leading to stiffness, swelling, and discomfort. The most common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
Osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease, is the most prevalent form of arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, resulting in bone-on-bone friction. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility.
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation. This type of arthritis can affect multiple joints simultaneously and often leads to chronic pain and joint deformity.
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It commonly affects the big toe and can cause intense pain, redness, and swelling.
Arthrosis: Understanding Joint Degeneration
Arthrosis, also known as osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. Unlike arthritis, arthrosis primarily affects the joints and does not involve systemic inflammation.
Arthrosis typically develops gradually over time and is associated with aging, joint overuse, previous joint injuries, and genetic factors. The most commonly affected joints include the hips, knees, hands, and spine. Symptoms of arthrosis include joint pain, stiffness, limited range of motion, and joint swelling.
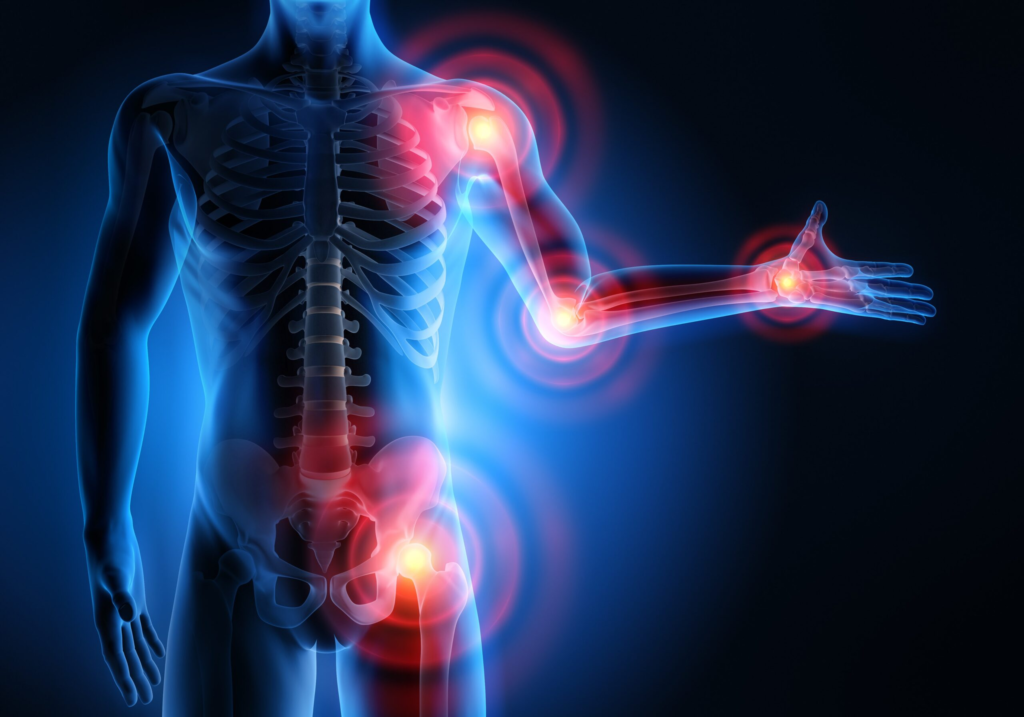
Managing Arthritis and Arthrosis
While there is no cure for arthritis or arthrosis, various treatments and lifestyle modifications can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Here are some general recommendations for managing these conditions:
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking can help strengthen the muscles around the affected joints and improve joint flexibility.
-
For Arthritis:
- Low-impact aerobic exercises:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Muscle-strengthening exercises:
- Light weightlifting
- Exercises with resistance bands
- Pilates
- Stretching:
- Yoga
- Tai Chi
- Gentle stretches
- Range of motion exercises:
- Gentle joint movements
- Low-impact dancing
For Osteoarthritis:
- Muscle-strengthening exercises:
- Light weightlifting
- Resistance exercises
- Progressive resistance training
- Low-impact aerobic exercises:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Range of motion exercises:
- Gentle joint movements
- Specific stretches for the affected joint
- Physical therapy:
- Sessions focused on strengthening and rehabilitation
- Hydrotherapy:
- Exercises performed in water, providing support to the joints
- Low-impact aerobic exercises:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, exacerbating symptoms. Losing weight can help reduce joint pain and slow down the progression of arthritis and arthrosis.
- Apply heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected joints can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Heat therapy is beneficial for relaxing muscles and improving blood circulation, while cold therapy can help numb the area and reduce swelling.
- Use assistive devices: Assistive devices such as canes, braces, or splints can provide support and stability to the affected joints, reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Consider natural supplements: Some individuals find relief from arthritis and arthrosis symptoms by incorporating natural supplements into their daily routine. One such supplement is Joint Genius, a 100% natural formulation designed to support joint health. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Remember, managing arthritis and arthrosis requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices. By understanding the differences between these conditions and taking proactive steps, you can better manage your joint health and improve your overall well-being.
Joint Genius is a natural supplement that may assist in supporting joint health. However, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or treatment.










2 Responses